Ongoing Lab Projects
-
Investigate the roles of PiCo, cNTS, and vagal afferents in swallow production and their coordination with breathing.
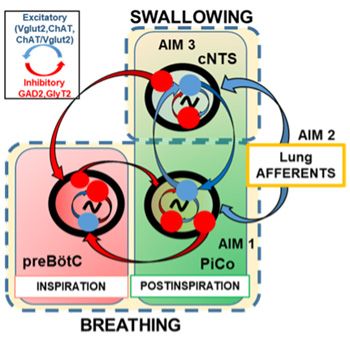
While there is some understanding about the importance of lung volume for mechanical coordination of swallow and breathing (Huff et al 2018 & 2020, Wheeler-Hegland et al 2001, McFarland et al 2016), little is known about central coordination. The swallow pattern generator (SPG) has been described as two half-center brainstem oscillators: 1) the dorsal swallow group, located within areas of the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS), and 2) the ventral swallow group (Jean 2001). The contributions of the rostral and caudal portions of the NTS (cNTS) in swallow pattern generation are not clear. Nearby in the brainstem, the preBötzinger complex (preBötC) inspiratory rhythm generator has been described in detail, but we have only begun to understand its involvement with the SPG. We previously reported that activation of the preBötC does not inhibit swallow production but delays swallow-related laryngeal closure (Huff et al 2022), increasing aspiration risk. The postinspiratory rhythm generator known as the postinspiratory complex (PiCo) (Huff et al 2016) has been suggested as a hub for swallow and laryngeal behaviors (Huff et al 2023), though its coordination with the SPG is unknown. The goal of this project is to 1) identify swallow generating neurons, 2) investigate interactions between the SPG and breathing centers, and 3) understand the role vagal afferents play.
2. Develop both anesthetized and freely behaving mouse preparations to characterize and evaluate the disturbances in swallow-breathing interaction and airway protection in Rett Syndrome.
Swallowing serves two physiological functions: passing food to the stomach for nutrition, and pharyngeal clearance for airway protection. During the developmental regression stage of classic (typical) Rett syndrome (RTT), disturbances in feeding and airway protective behaviors occur as early as a few months of age with most occurring after 2 years (Motil et al 2012, Abraham et al 2015, Sideris et al 2023). These disturbances cause an increased prevalence of chronic malnutrition and respiratory infection (MacKay et al 2018, Lotan et al 2006). In a questionnaire distributed by the International Rett Syndrome Foundation (IRSF), 81% of parents reported moderate to severe feeding/swallowing problems (dysphagia) (Motil et al 2012). Penetration and aspiration of food, liquid, and mucus into the airway, resulting in recurring bouts of aspiration pneumonia, was reported in 67-94% of RTT children (Abraham et al 2015, Sideris et al 2023, Anderson et al 2014, Motil et al 1999). It is unknown how mutation to the MECP2 gene, resulting if deficiency of mecp2 protein, results in disruption to feeding and airway protection. The goal of this project is to develop a preclinical mouse model to characterize and evaluate swallow-breathing interaction and airway protection in Rett Syndrome.
Methods used for ongoing projects
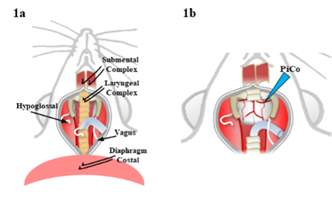
1.In-vivo freely breathing anesthetized approach both (a) without and (b) with ventral brainstem access. Water triggered swallow and breathing characteristics are measured via EMGs of the diaphragm, submental and laryngeal complex and ENGs of the hypoglossal and vagus. Utilizes both chemogenetics and optogenetics
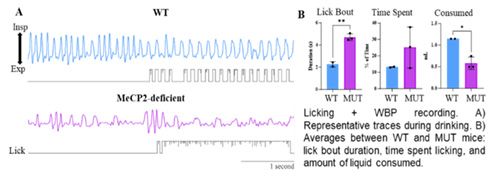
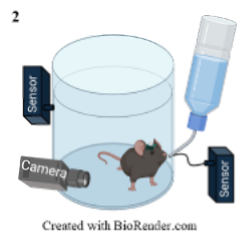
2. Awake and alert whole body plethysmography (WBP) is a well-established technique to measure ventilatory patterns during various states. Our novel technique combines WBP, a lick sensor, and video recording to detect behavior and ventilatory patterns during drinking and assess coordination of licking and breathing.
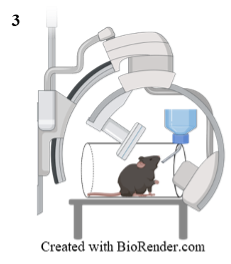
3. Awake and alert Videofluoroscopic Swallow Studies (VFSS) (i.e. Clinical Swallow Study) to evaluate swallow function, assess penetration and aspiration of food/liquid, and diagnose dysphagia. This is regularly adapted for use in large animal and rodent models to assess swallow function in basic science settings. Mice will drink an iohexol, iodine-based contrast, sugar water solution within a mini c-arm as is consistent with VFSS.